Transformers play a crucial role in power transmission and distribution across residential, commercial, and industrial settings. However, like any electrical device, transformers are not immune to faults. When left unchecked, transformer issues can result in system failure, production downtime, or even electrical fires. Knowing how to identify and address common transformer faults is essential for ensuring safety, reliability, and longevity.
In this guide, we’ll explore the most frequent transformer problems, the symptoms to watch for, and practical solutions to keep your equipment running efficiently.
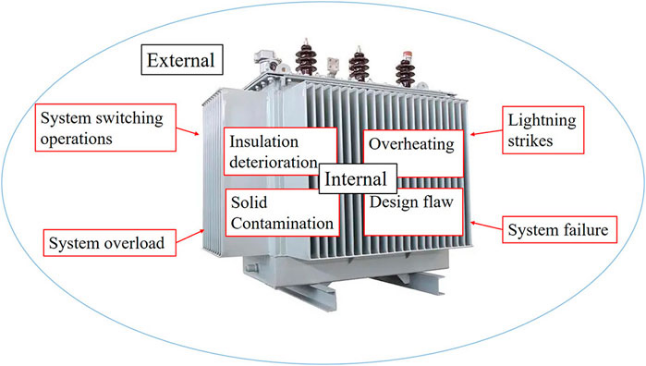
Why Transformer Fault Diagnosis Matters
A transformer fault, even a minor one, can escalate into significant damage if not addressed promptly. Understanding the warning signs and root causes allows engineers and maintenance teams to:
- Prevent unplanned outages
- Extend transformer lifespan
- Avoid costly repairs or replacements
- Ensure operator safety
- Maintain system efficiency
1. Overheating
Symptoms:
- Hot spots detected via infrared scans
- Oil discoloration in oil-cooled transformers
- Protective relay trips
- Strange smell (burnt insulation)
Causes:
- Overloading
- Poor ventilation or cooling system failure
- Internal short circuits
- Ambient temperature too high
Solutions:
- Check transformer loading and reduce if necessary
- Inspect and repair or clean fans, radiators, and cooling ducts
- Install temperature sensors or alarms
- Ensure installation environment is well-ventilated
2. Insulation Failure
Symptoms:
- Dielectric test failure
- Visible cracks in bushings
- Low insulation resistance readings
- Tripping during startup
Causes:
- Aging insulation
- Moisture ingress
- Overvoltage or lightning strikes
- Poor quality maintenance
Solutions:
- Perform insulation resistance tests regularly
- Dry the transformer windings (oven drying or vacuum drying)
- Replace damaged insulation or bushings
- Ensure proper sealing and weatherproofing
3. Oil Leaks (in Oil-Immersed Transformers)

Symptoms:
- Visible oil stains or puddles
- Low oil level in conservator tank
- Drop in dielectric oil pressure
Causes:
- Corrosion of gaskets and seals
- Physical damage to the tank
- Overheating causing pressure build-up
Solutions:
- Identify leak source and replace gaskets or fittings
- Weld or patch small tank cracks
- Regularly check oil levels and top up with matching dielectric oil
4. Partial Discharge
Symptoms:
- Audible hissing or crackling sounds
- Radio frequency interference
- Deterioration of insulation
- Detection via specialized test equipment
Causes:
- Voids or air bubbles in insulation
- Contaminants like dust or moisture
- Loose connections
Solutions:
- Use partial discharge detection tools (e.g., PD detectors, ultrasonic testers)
- Clean and dry the internal components
- Tighten all electrical connections
- Replace faulty insulation or windings
5. Short Circuit (Winding Faults)
Symptoms:
- Sudden loss of voltage
- Fuse or breaker tripping
- Smoke or burning smell
- Severe overheating
Causes:
- Electrical surges
- Mechanical stress from overload
- Manufacturing defects
- External fault (e.g., lightning)
Solutions:
- Conduct a winding resistance or turns ratio test
- Isolate and test each winding
- Repair or replace the damaged winding
- Consider surge protection devices
6. Noisy Operation
Symptoms:
- Buzzing or humming sounds louder than usual
- Vibration felt on enclosure
Causes:
- Loose core laminations
- Magnetostriction in the core
- Mechanical wear over time
- Resonance with other machinery
Solutions:
- Tighten bolts and fasteners
- Add sound dampeners or vibration isolators
- Re-stack or replace loose core laminations
- Install the transformer away from sensitive areas
Note: Some noise is natural; look for sudden changes or volume spikes.
7. Moisture Contamination
Symptoms:
Decrease in insulation resistance
Reduced oil dielectric strength
Rust on internal components
Unstable transformer behavior in humid conditions
Causes:
Breather system failure
Seal cracks or tank leaks
Poor storage or handling of spares
Solutions:
Use moisture absorbers like silica gel and maintain breathers
Dry the transformer internally using heating or vacuum methods
Test and replace oil if water content is high
8. Incorrect Tap Changer Settings
Symptoms:
Output voltage too high or too low
Phase imbalance
Poor power quality
Causes:
Manual error
Faulty tap changer mechanism
Control system malfunction
Solutions:
Verify and reset tap positions based on load requirements
Perform mechanical inspection of tap changer
Lubricate or replace worn-out contacts
Important: Always make tap changes with the transformer de-energized (unless it’s an On-Load Tap Changer).
Routine Maintenance Tips to Prevent Transformer Failures
Perform annual oil testing (dielectric strength, moisture, acidity)
Conduct thermal imaging twice a year
Schedule insulation resistance and winding tests regularly
Keep surroundings clean and moisture-free
Maintain a log of operating temperatures and load behavior
Conclusion
Understanding the most common transformer faults and how to fix them helps electrical engineers and facility managers maintain safer, more reliable power systems. Regular inspections, condition monitoring, and preventive maintenance are the best defense against catastrophic transformer failure.
A proactive approach not only saves time and money—it also protects lives, equipment, and productivity.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SANAKY VIETNAM., CO LTD - Manufacturer of Chest Freezer - Upright Cooler, Transformer, RO Water Purifier...
Website: www.sanaky-vn.com
Hotline: (+84) 986123903
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese  English
English  Chinese
Chinese  French
French  Spanish
Spanish  Russian
Russian  Arabic
Arabic  Portuguese
Portuguese