Transformers are indispensable components of any industrial power system, used to step up or step down voltage levels to ensure efficient and safe power distribution. However, operating transformers—especially high-capacity units in factory or industrial environments—requires strict adherence to safety procedures. A failure to follow these guidelines can lead to electrical accidents, fires, equipment damage, and even fatalities. In this article, we’ll walk you through the essential safety guidelines for operating transformers in industrial settings, helping you ensure safe and uninterrupted power flow.
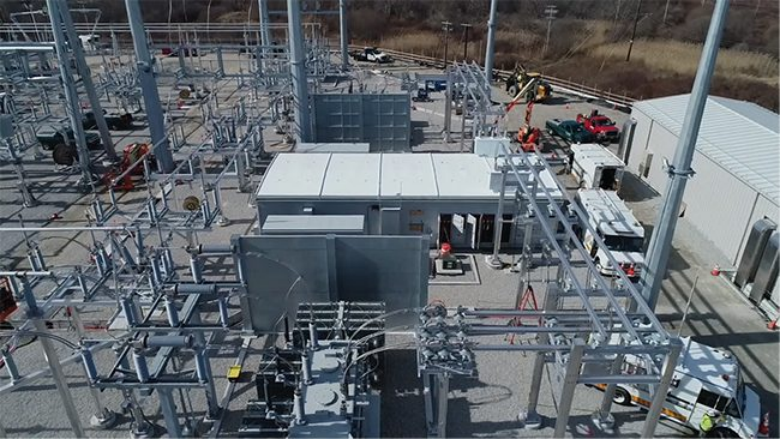

Why Transformer Safety Matters in Industrial Plants
Industrial transformers typically handle high voltages and currents, often in challenging environments. Improper handling or a lack of safety protocol can result in:
- Equipment malfunction
- Power outages
- Fire hazards
- Electric shocks or electrocution
- Legal and insurance issues
Whether it’s a dry-type transformer inside a building or an oil-immersed transformer installed outdoors, safety is non-negotiable.
1. Pre-Installation Safety Checks
Before a transformer is even energized, you must:
- Verify proper grounding: Ensure that both the primary and secondary sides of the transformer are properly grounded to avoid electrical shock or damage due to voltage surges.
- Inspect insulation: Check the integrity of insulation on all wires and cables. Moisture, aging, or physical damage can make the unit unsafe.
- Confirm ratings: Make sure the voltage and current ratings of the transformer match the load requirements and the grid standards.
- Environmental safety: Install the transformer in a location that is dry, well-ventilated, and away from flammable materials or gases.
2. Safety During Transformer Installation
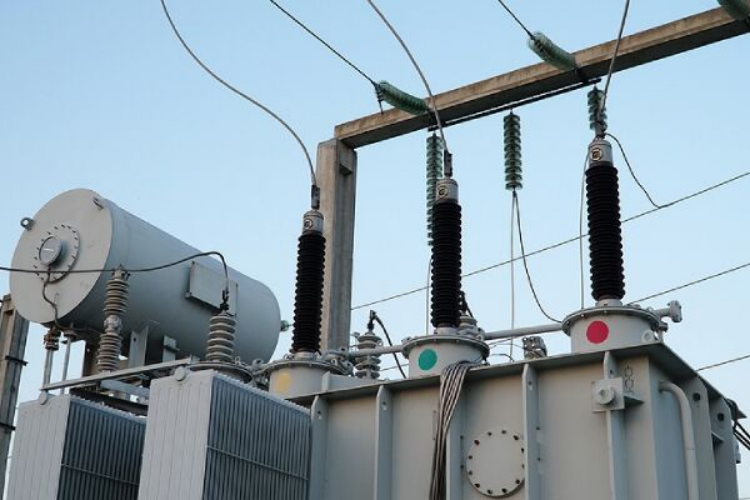

Transformer installation should be handled by qualified personnel. Best practices include:
- Use of personal protective equipment (PPE): Gloves, arc-rated clothing, face shields, and safety boots should be mandatory for all technicians.
- Proper lifting and handling: Use cranes or forklifts to handle large transformers, following weight distribution guidelines to avoid damage.
- Isolation of power: Ensure the circuit is fully de-energized before connecting the transformer.
- Labeling and warning signs: All terminal boxes and input/output points must be clearly labeled. Safety signage must be displayed near high-voltage equipment.
3. Energizing the Transformer Safely
Once installed, energizing a transformer must follow a step-by-step process:
- Initial testing: Use a megohmmeter to test insulation resistance and ensure no winding short circuits exist.
- No-load test: Before connecting any load, energize the transformer and monitor its behavior—noise, heat, oil levels (for oil transformers), and voltage stability.
- Phase checks: Ensure correct phase sequencing and grounding are in place.
- Monitoring: Use thermal cameras or sensors to observe abnormal heating.
4. Operational Safety Practices
Transformers in operation must be regularly monitored and maintained. Key practices include:
a. Routine Inspections
Schedule regular inspections for:
- Oil leakage (in oil-type transformers)
- Unusual noise or vibrations
- Bushing cracks or discoloration
- Loose connections
- Cooling system effectiveness
b. Temperature Monitoring
Overheating is a common failure point. Industrial transformers should be equipped with temperature sensors and alarms to monitor winding and oil temperatures. Operating above the rated temperature shortens the transformer’s lifespan and increases the risk of fire.
c. Load Management
Avoid overloading the transformer. Continual overloading results in excessive heating and insulation damage. Use load tap changers, where applicable, to adjust output voltage safely.
5. Transformer Oil Handling Safety (for Oil-Immersed Units)

If your factory uses oil-filled transformers:
- Use only dielectric transformer oil approved for high-voltage equipment.
- Regularly sample and test oil for dielectric strength, moisture, and acidity.
- Ensure oil tanks are sealed and equipped with conservators or breathers to prevent moisture ingress.
- Never handle oil near open flames or high temperatures.
6. Emergency Procedures
Every industrial plant should have emergency protocols for transformer failures. These include:
- Automatic shutdown systems: Circuit breakers and relays should automatically disconnect the transformer if faults are detected.
- Fire suppression systems: Install fire extinguishers (Class C for electrical fires) and fire-resistant barriers around transformer rooms.
- Evacuation plans: Train staff on emergency response and ensure easy access to exits.
- Incident reporting and investigation: Maintain logs of all incidents and perform root-cause analyses.
7. Maintenance Protocols for Long-Term Safety
Long-term safety is dependent on preventive maintenance. Include the following in your maintenance schedule:
- Visual inspections every week
- Electrical testing (e.g., insulation resistance, turns ratio) every 6-12 months
- Oil testing every 12 months
- Infrared thermal scans every quarter
- Complete transformer servicing every 2-3 years
Use condition monitoring tools to detect early signs of deterioration.
8. Staff Training and Safety Awareness
Lastly, human error is often the cause of transformer-related accidents. Make sure:
- Only certified electricians or engineers operate or maintain transformers.
- Regular training sessions are conducted on electrical safety.
- All safety protocols are documented and easily accessible.
- Mock drills are held to prepare for emergency scenarios.
Conclusion: Safety First, Always
Transformers play a vital role in powering factories and industrial machinery. But with great power comes great responsibility. By following a robust safety framework—starting from installation to operation and maintenance—you minimize risk, protect human life, and enhance the longevity of your equipment.
When safety becomes part of your operational culture, the entire plant benefits—from reduced downtime and lower repair costs to compliance with regulatory standards.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SANAKY VIETNAM., CO LTD - Manufacturer of Chest Freezer - Upright Cooler, Transformer, RO Water Purifier...
Website: www.sanaky-vn.com
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese  English
English  Chinese
Chinese  French
French  Spanish
Spanish  Russian
Russian  Arabic
Arabic  Portuguese
Portuguese